Bagosus nodulosus
(Gyllenhal, 1836)
Flowering-Rush Weevil

Aquatic Coleoptera
Conservation Trust
OVERVIEW
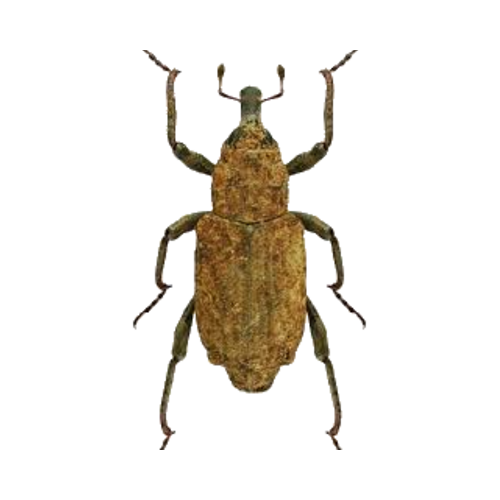

Bagosus nodulosus is an extremely rare aquatic weevil belonging to the family Curculionidae. This specialist species is entirely dependent on flowering rush (Butomus umbellatus) for its survival, with larvae developing within the plant's flower heads. As one of Britain's most endangered aquatic beetles, it represents a critical indicator of healthy aquatic plant communities.
CONSERVATION STATUS
Key Threats:
- Decline and fragmentation of flowering rush populations
- Water pollution and eutrophication
- River management and channelization
- Invasive plant species competition
- Climate change affecting aquatic plant communities
Population Trend:
DISTRIBUTION
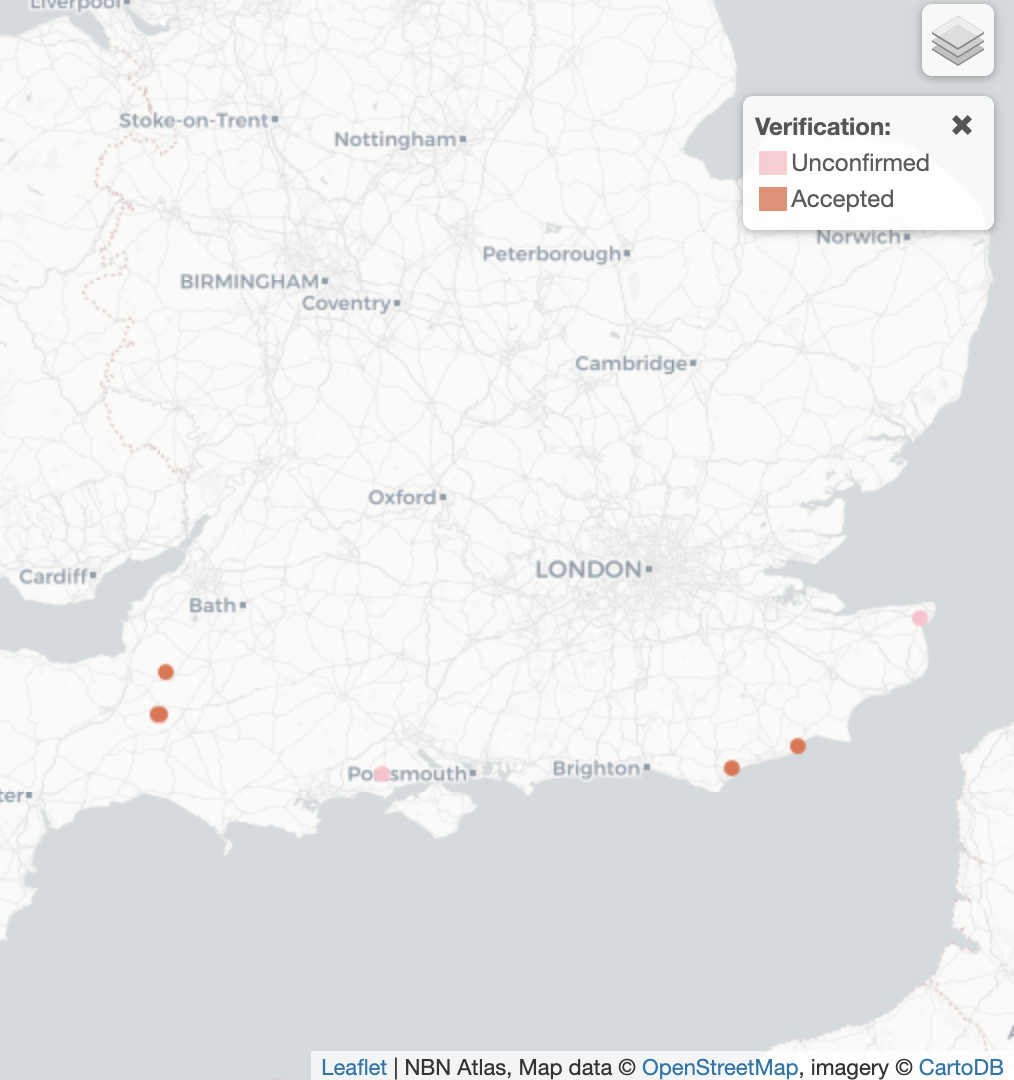
Current Range: Extremely limited to very few water bodies in southern England, primarily in Thames Valley and adjacent areas where flowering rush populations remain healthy.
Habitat Distribution: Exclusively associated with established flowering rush beds in slow-flowing rivers, canals, and well-vegetated lakes with high water quality and minimal disturbance.
ECOLOGY & HABITAT
Slow Rivers
Slow-flowing rivers with established flowering rush colonies
Flowering Rush
Exclusive dependence on Butomus umbellatus for reproduction
Clean Water
High water quality essential for flowering rush health
Life Cycle: Complete metamorphosis with larvae developing exclusively in flowering rush flower heads and seed capsules
Diet: Adults and larvae feed exclusively on flowering rush tissues, particularly reproductive structures
Host Specialization: Entirely dependent on healthy flowering rush populations for reproduction and survival
CONSERVATION ACTIONS
Host Plant Protection
Protect and restore flowering rush populations in key waterways
Water Quality
Maintain high water quality to support healthy aquatic plant communities
Habitat Management
Manage river banks and margins to prevent invasive species encroachment
Population Monitoring
Regular surveys of known sites and search for new populations