Bidessus minutissimus
(Germar, 1824)
Minutest Diving Beetle

Aquatic Coleoptera
Conservation Trust
OVERVIEW
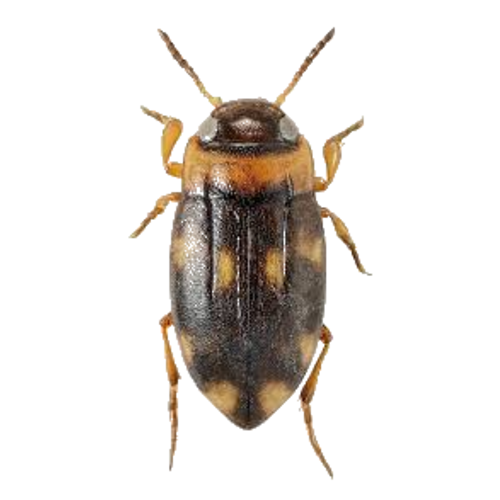

Bidessus minutissimus is a tiny diving beetle belonging to the family Dytiscidae, living up to its name as one of Britain's smallest aquatic beetles. This specialist species is adapted to acidic, nutrient-poor waters in heathland and moorland environments, where it plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of these unique aquatic communities.
CONSERVATION STATUS
Key Threats:
- Heathland habitat loss and fragmentation
- Drainage and water table changes
- Nutrient enrichment and eutrophication
- Climate change affecting upland water levels
- Acidification changes due to atmospheric pollution
Population Trend:
DISTRIBUTION
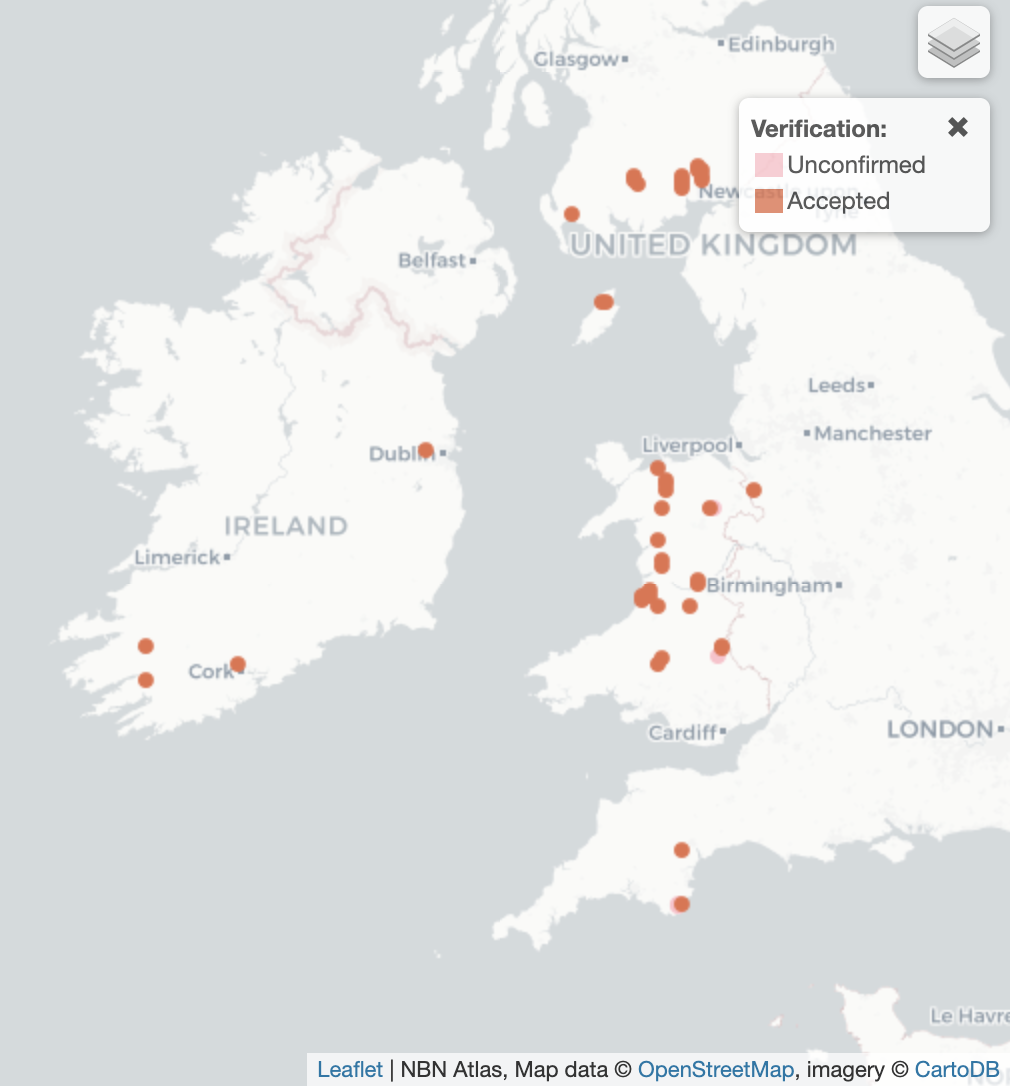
Current Range: Scattered distribution across northern England, Wales, and Scotland, primarily in upland heathland and moorland areas with suitable acidic water bodies.
Habitat Distribution: Found in acidic bog pools, flushes, seepage areas, and shallow acidic ponds in heathland and moorland environments, particularly those with Sphagnum moss and low nutrient levels.
ECOLOGY & HABITAT
Acidic Pools
Shallow bog pools and flushes with low pH and nutrients
Heathland
Open heathland with scattered pools and seepage areas
Sphagnum Moss
Moss-dominated margins providing shelter and microhabitats
Life Cycle: Complete metamorphosis with both larvae and adults aquatic, adapted to acidic conditions
Diet: Predatory - feeds on small invertebrates, mites, and organic particles in the water column
Acid Adaptation: Specialised physiology allows survival in low pH environments that exclude many competitors
CONSERVATION ACTIONS
Heathland Protection
Protect and restore heathland and moorland habitats
Hydrology Management
Maintain natural water levels and prevent drainage
Water Quality
Prevent nutrient enrichment and maintain acidic conditions
Survey & Monitoring
Regular monitoring of populations and habitat condition